In this article, I will discuss the Why Biodiversity Matters. Biodiversity is the huge mix of plants, animals, fungi, and tiny microbes that keep Earths systems running and make everyday life possible for people.
It helps stabilize climates, cleans the air and water, and provides food and medicines we all rely on. Seeing how much we gain from this variety can motivate us to protect nature so coming generations inherit a healthy planet.
What is Biodiversity ?
Biodiversity is the huge mix of living things that share our planet. It includes everything from towering trees and tiny insects to developing fungi and germs you cant even see.

Biodiversity covers three main layers: the slight genetic differences inside a species, the different species you can spot in the park or ocean, and the many habitats they build together, like forests, reefs, and deserts.
Having this variety keeps nature working well; it makes sure flowers get pollinated, dirt stays rich, and weather patterns stay steady. A healthy pool of plants and animals also gives people what we need to live every day-food, medicine, and the clean air and water we sometimes take for granted.
Why Biodiversity Matters
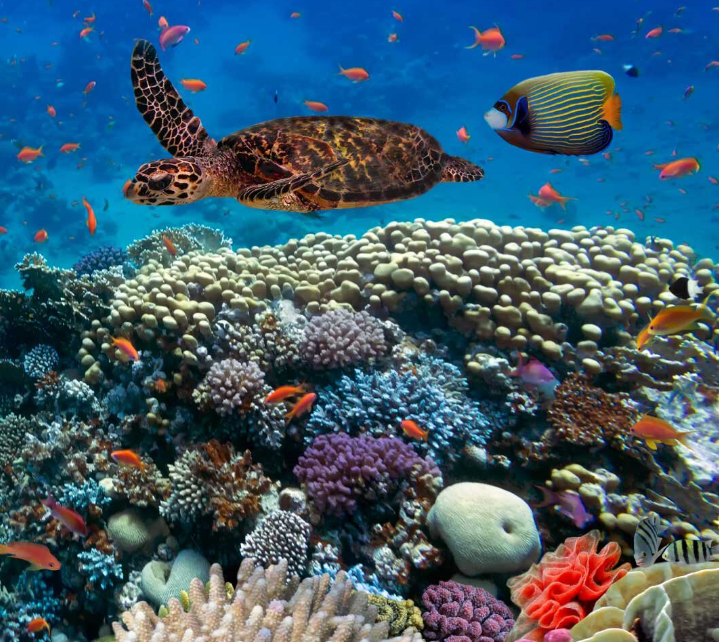

Ecosystem Stability: A wide range of plants and animals makes nature stronger, so forests, lakes, and soils bounce back faster when they are troubled.
Food Security: More species mean more types of grains, fruits, livestock, and fish, giving communities around the world the meals they need to grow healthy.
Medicinal Resources: Countless medicines start with ingredients pulled from the leaves of a plant, the scale of a bug, or even bacteria living in wet soil.
Climate Regulation: Lush, diverse habitats store huge amounts of carbon, cool the air, and help clouds form, all of which steady the planets climate.
Clean Air and Water: Wetlands, reefs, and forests act like natural filters, trapping waste so we can breathe easier and drink cleaner water.
Economic Benefits: Farmers, fishermen, tour guides, and many small businesses depend on vibrant ecosystems, so nature keeps local wallets and whole economies afloat.
Cultural and Recreational Value: Myths, festivals, hiking trails, and quiet fishing spots draw meaning and joy from the plants and animals sharing our land.
Adaptation and Survival: Varied genes within a single species act like spare tires; when conditions shift, some individuals can still carry the group through.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Stability
Biodiversity, or the variety of life on our planet, plays a huge role in keeping ecosystems stable . Different plants, animals, and tiny organisms all do their own job-whether its recycling nutrients, pollinating flowers, or forming healthy soil.
Because of this teamwork, nature can bounce back when it gets a big hit, like a hurricane, a disease, or even slow changes in the climate. When many species share a space, they help control population numbers and keep food chains running smoothly.
But if species disappear, those safety nets start to fray and whole systems can topple. thats why protecting biodiversity is crucial if we want ecosystems that keep supporting life on Earth for years to come.
Benefits of Biodiversity to Humans
Food Security
Diverse species give us many crops, animals, and fish that keep our diets healthy.
Medicinal Resources
Plants and animals are the basis for countless medicines and drug ingredients.
Clean Air and Water
Forests, wetlands, and reefs filter waste and keep our air and water clear.
Climate Regulation
Healthy habitats store carbon and help balance rainfall and temperature around the globe.
Economic Support
Tourism, fishing, farming, and more depend on rich nature for jobs and income.
Cultural Value
Parks, wildlife, and even local legends shape art, beliefs, and fun activities people cherish.
Ecosystem Services
Biodiversity keeps soil fertile, moves pollen, and controls pests at no extra cost to farmers.
Biodiversity and Climate Regulation
Biodiversity is like nature’s safety net when it comes to climate control. Forests, wetlands, and oceans filled with many different plants and animals gulp up huge amounts of carbon dioxide and store it away, acting as giant carbon sponges.
When these ecosystems are strong, they help steady weather at both local and global levels, so we see fewer wild storms, floods, or long dry spells.
A mix of plant species also keeps soil rich and lets it hold more water, which makes communities better able to bounce back when the climate swings. For a safe future, we have to protect this living variety; doing so cuts climate risks and helps people, wildlife, and the planet stay in balance.
Conservation Efforts and Sustainable Practices
Protected Areas: Parks, wildlife reserves, and ocean sanctuaries are set up to keep animals safe at home.
Habitat Restoration: People replant trees, clean up wetlands, and fix broken nature spaces so life can return.
Sustainable Agriculture: Farmers use earth-friendly tricks that keep soil healthy and cut back on harsh chemicals.
Legislation and Policies: Strong laws now target poaching, illegal logging, and messy trash so nature gets real backup.
Community Involvement: Local groups team up in caring for land and water, making sure everyone shares the load.
Education and Awareness: Classes, trips, and campaigns explain why rich nature matters and how we can act right.
Supporting Renewable Energy: Wind, solar, and other clean power lighten the climate load and spare wild places from harm.
Pros & Cons
| Pros | Cons |
|---|---|
| Protects endangered species and habitats | Can be costly to implement and maintain |
| Maintains ecosystem balance and services | May restrict land use and development |
| Supports long-term food security | Requires cooperation across multiple sectors |
| Enhances climate change mitigation | Enforcement of laws can be challenging |
| Promotes sustainable livelihoods for locals | Initial resistance from industries or communities |
| Improves soil, water, and air quality | Conservation efforts can take time to show results |
| Raises public awareness and education | Conflicts may arise over resource use |
Conclusion
Biodiversity is the web of different plants, animals, fungi, and tiny life forms that keeps nature running smoothly.
Every type of organism has a job, whether that’s pollinating crops, cleaning water, or storing carbon. More variety in species makes ecosystems sturdier, so they bounce back faster after storms, fires, or even pollution.
Yet farms, cities, and unchecked pollution chip away at these groups, tipping the balance that supports us. Defending biodiversity isn’t a distant luxury; it’s a practical step toward clean air, healthy soil, and a climate we can live with.