In this article, I will explain How to Open Command Prompt on Windows in a simple way and in a manner that will not take a lot of time.
Command Prompt, also known ask CMD, is a utility application that enables a user to manage a computer and its tasks, diagnose potential problems, and perform different sets of instructions.
No matter whether you are a novice or a seasoned computer user, understanding different ways of accessing CMD can enhance productivity and help you save time.
About Command Prompt
Command Prompt is a command-line tool present in almost all versions of Windows. Windows has many functions that can be performed through the graphical interface, however, through cmd, which is the more popular name, these functions can also be executed in a much simpler way.

One only needs to type the relevant command. Windows functions like files, programs and issues can be managed through text.
For experts, it is extremely beneficial since many times there is a need to automate tasks, identify issues as well as adjust settings to streamline the processes. IT experts and developers find it comparatively easier to use typed commands rather than dealing with automation tools.
How to Open Command Prompt on Windows
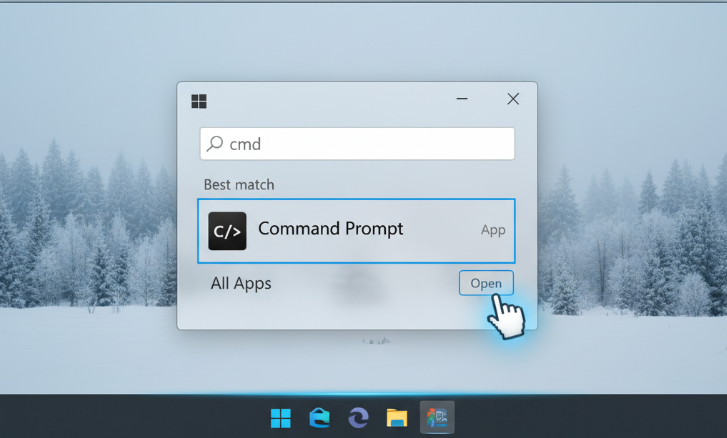
Here’s a clear step-by-step example of how to Open Command Prompt on Windows:
- Press Windows Key on your keyboard or click the Start Menuled at the bottom left of your screen.
- In the search window, type either cmd or the whole Command Prompt.
- Command Prompt will come up among the results.
- Click to access it the usual way.
- In case you require administrator access, right click Command Prompt and click on Run as administrator.
- A User Account Control (UAC) may pop up, click Yes to grant permission.
- A Command Prompt window appears with a dark screen and a blinking cursor.
- You can input commands, e.g a
dircommand to display the files or an ipconfig command to access network information. - To close Command Prompt, type exit and hit Enter or click on the X in the upper right.
Tips for Faster Access
Below are some suggested procedures for achieving faster access to the Command Prompt.
Pin to Taskbar – It’s possible to access the Command Prompt with a single click after right-clicking the Command Prompt icon and then selecting the pin to the taskbar option.
Pin to Start Menu – Right-clicking the Command Prompt icon and selecting it allows for Command Prompt to be accessed from the Start Menu.
Create Shortcuts – By right-clicking the desktop and selecting new and then shortcut it is possible to create a shortcut which can be named and is done after entering the command cmd.exe.
Keyboard shortcut – A desktop shortcut can be made to which a key or set of keys can be assigned to open it by right-clicking the desktop shortcut and then selecting assign shortcut.
Windows Terminal – The windows terminal can be accessed by the command windows plus X and subsequently the Command Prompt can be selected.
Risk & Considerations When Using Command Prompt
You’ve created a section titled Risks & Considerations when using Command Prompt.
Accidental System Changes
In Command line, a user can change and modify config files system files or even change the system settings. A user can modify the system’s integrity and stability by running some commands without knowledge of their effect.
Administrator Privileges
Open CMD with administrative commands to have total control of the system. There is a fear of having unobserved changes and, unassessed security breaches.
Malware Risk
There are many unverified and untrusted blogs or sites that could have a Command Prompt or CMD based Malware, Viruses and other Cyber Threats.
Data Loss
When a user uses the command ‘del’, ‘format’, or others, they can wipe out the files, which might be important.
Lack of Options
In Command Prompt, the “undo” command is not responsive. Mistakes with the system could be catastrophic and thus the user is urged to double and triple check their commands that they are sure that they are right before executing them.
Use Cases for Security
Network Troubleshooting: Use commands such as ‘ping’, ‘tracert’, and, ‘netstat’ to locate unauthorized access or troubleshoot network problems.
User Account Management: An administrator can secure access and create, change, or revoke user accounts with the net user command.
Folders and Files: Use the command icicles to analyze, change, and ensure classified information is secure.
Malware Detection and Removal: Monitor suspicious and unrecognizable processes with the command task list and get rid of them with the command task kill.
Audit System Logs: Use evenward or wevtutil and check the system logs for suspicious behavior or hack attempts.
Secure File Deletion: Use the command cipher /w to delete irreversible sensitive classified files to prevent unauthorized access and data recovery.
Conclusion
When you understand the approach, beginning Command Prompt using the different quadrants/interface/ programs is simple enough on the Start Menu, using the Start Tab, using the Run box, going through the File Explorer, or even creating shortcuts.
Advanced tasks or troubleshooting, running Command Prompt as an System Administrator is a an unrelated but rather essential, skill set. Anyone can use the given tips and their achieve a good command over the tip.
CMD is a valuable asset when system managing, troubleshooting the network, or running system and network security. First time users or veteran Windows users can take equal advantage of it.
FAQ
How do I open Command Prompt quickly?
You can open it via the Start Menu, Run dialog (Win + R → type cmd), File Explorer (Shift + Right-Click → “Open Command Window Here”), or create a desktop shortcut.
How do I open Command Prompt as an administrator?
Right-click Command Prompt in the Start Menu or search results, then select Run as administrator and confirm the User Account Control prompt.
Is there a faster way to access Command Prompt frequently?
Yes. Pin CMD to the Taskbar or Start Menu, create a shortcut with a keyboard hotkey, or use Windows Terminal with a Command Prompt tab.
Can opening CMD harm my computer?
Only if you run harmful commands or scripts. Always double-check commands and avoid executing untrusted scripts.